HashMap扩容机制
风力掀天浪打头,只须一笑不须愁。
HashMap存储原理与扩容机制
存储方式
数组
使用 Node 数组存储各个元素,Node 类实现了 Map.Entry。
链表
尾插法链接到 table [ slot ] 节点后面。
红黑树
扩容时机
map 容器添加元素方法
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
无论何种情况下发生扩容,table [ ] 长度始终为 2 的幂。
newCap = oldCap << 1
table.length == 0
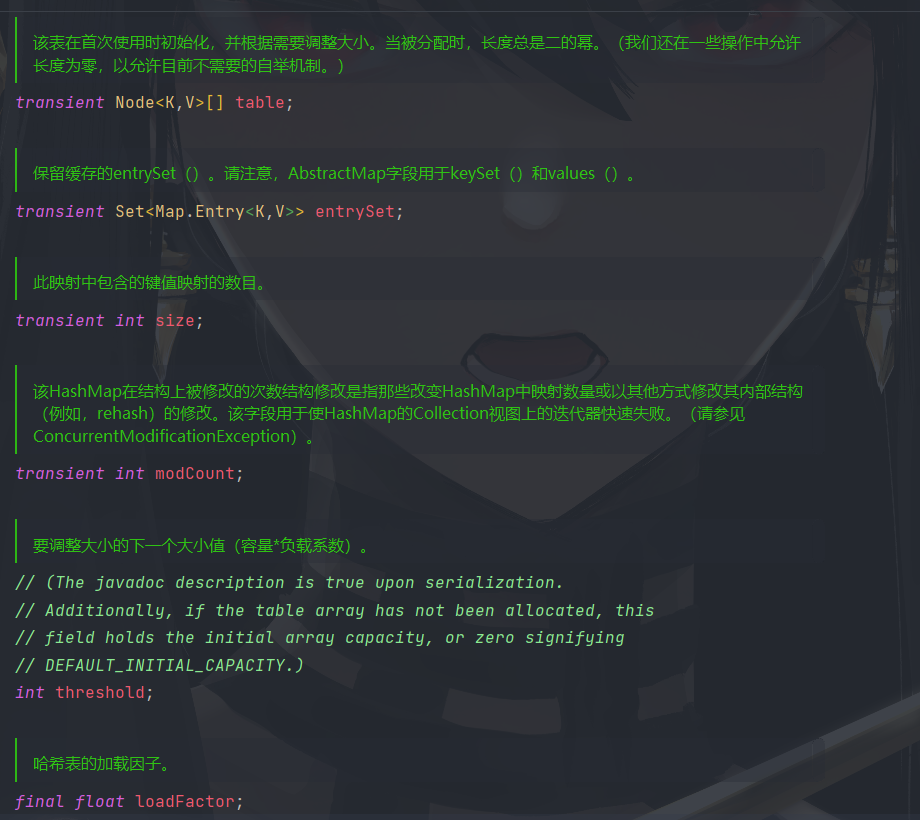
空参创建 HashMap 时第一次往 map 中 put 会发生扩容,扩容到默认大小 16
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
测试案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("k1", "v1");
}
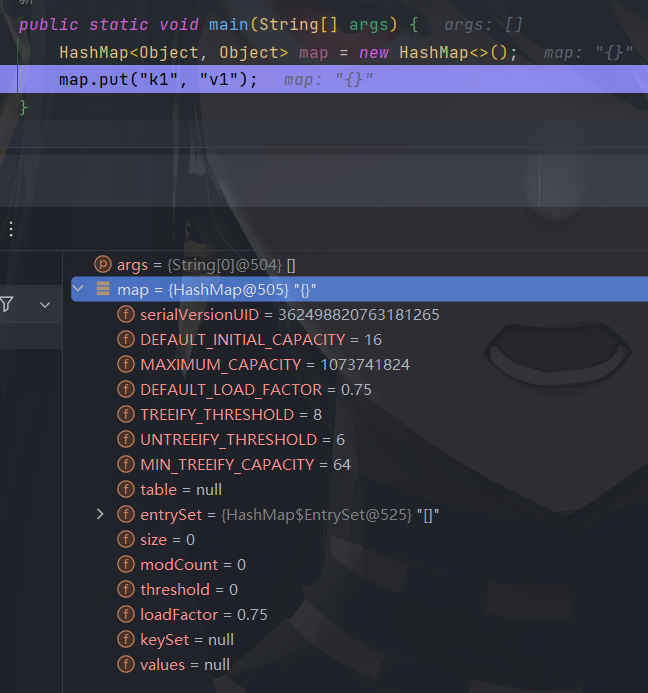
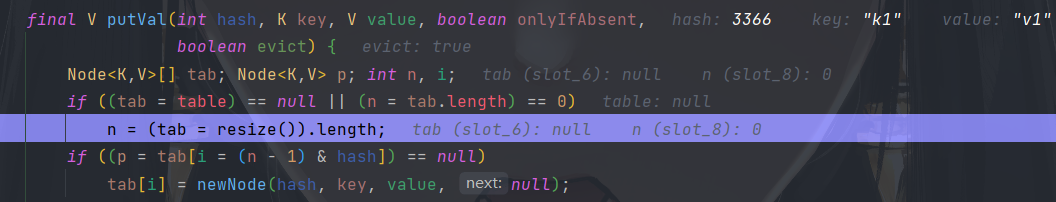
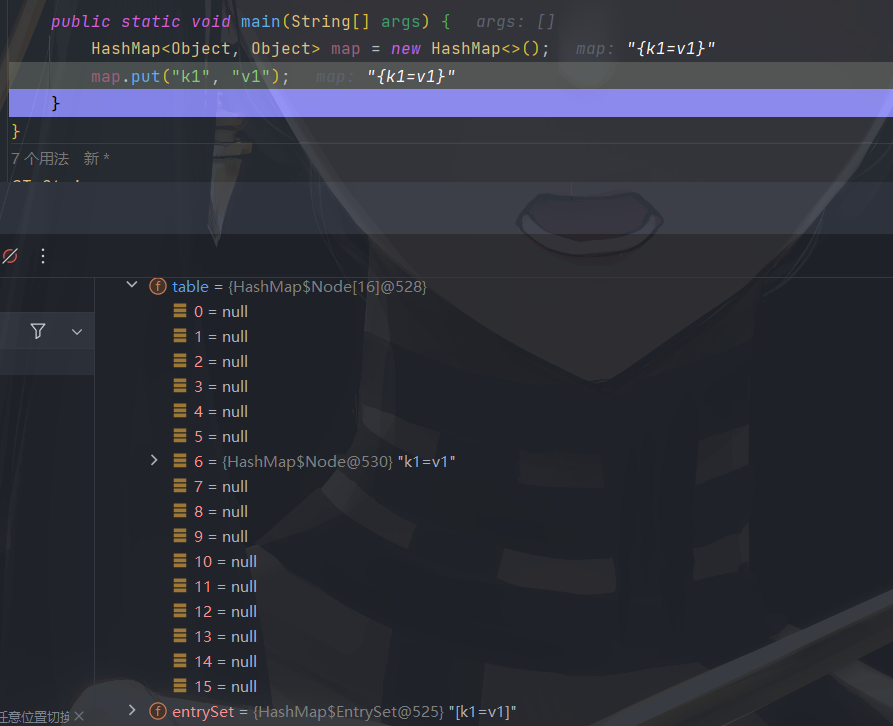
table.length * loadFactor <= map.size()
当前 map 容器中元素总量大于等于 table [] * 加载因子,发生扩容。
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
测试案例:
@Test
public void test1() {
HashMap<User, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (; i < 12; i++) {
map.put(new User(i), i);
}
map.put(new User(i), i++);
System.out.println(map);
}
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
class User {
private int id;
private static int x = 0;
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return x++; // x < map.size()时, 使每个新创建的 User 对象都被散列到不同槽位,方便观察
}
}
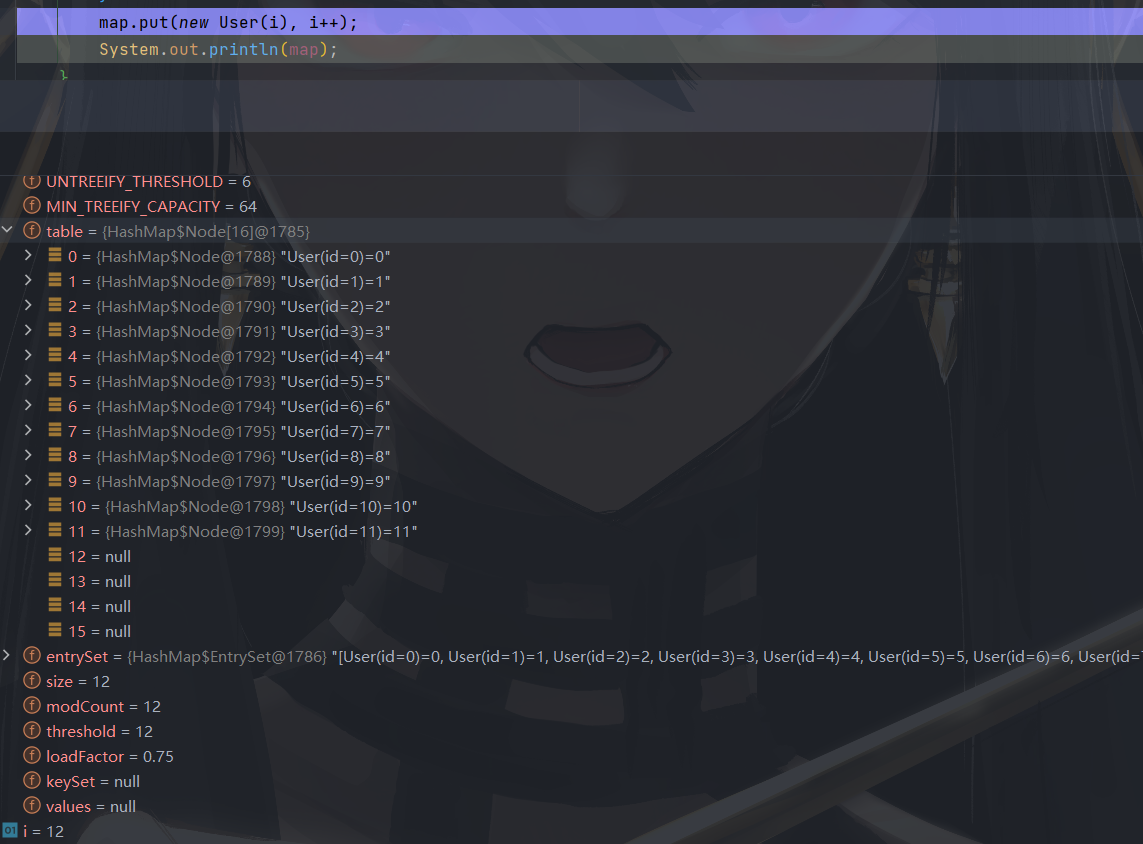
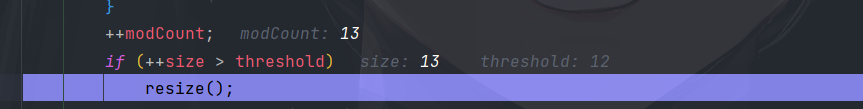
8 <= slot.length && table.length <= 64
当前 table [ ] 中某一槽位的链表长度 >= 8 ,并且 table.length <= 64 时,链表不会发生树化,而是进行一次扩容。
测试案例:
逐次往 map 容器的 table[ 0 ] 链接元素,观察链表树化、扩容时机。
@Test
public void test2() {
HashMap<User, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (; i < 8; i++) {
map.put(new User(i), i);
}
// 将 table 数组扩容到 32 (16 >> 1)
map.put(new User(i), i++);
// 将 table 数组扩容到 64 (32 >> 1)
map.put(new User(i), i++);
// 树化链表
// slot[hash].length > 8 : 当前链表长度(不包括待加入节点) >= 8
// table.length >= 64 : 当前 Node 数组长度 >= 64
map.put(new User(i), i++);
System.out.println(map);
}
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
class User {
private int id;
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return 0; // 使每个新创建的 User 对象都被散列到相同的槽位 0 ( 0 & any = 0 )
}
}
往 map 容器中添加 8 个元素,并且 8 个元素均落到 table[ 0 ]
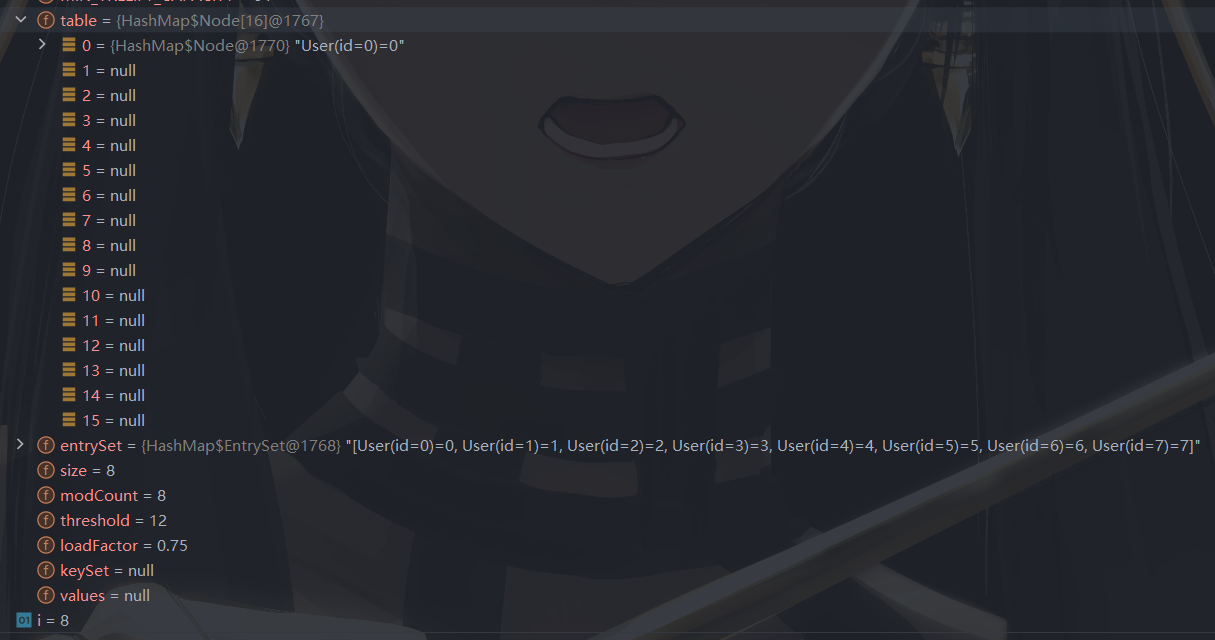
继续添加元素,此时 table[ 0 ]length ==8 ,尝试进行树化。
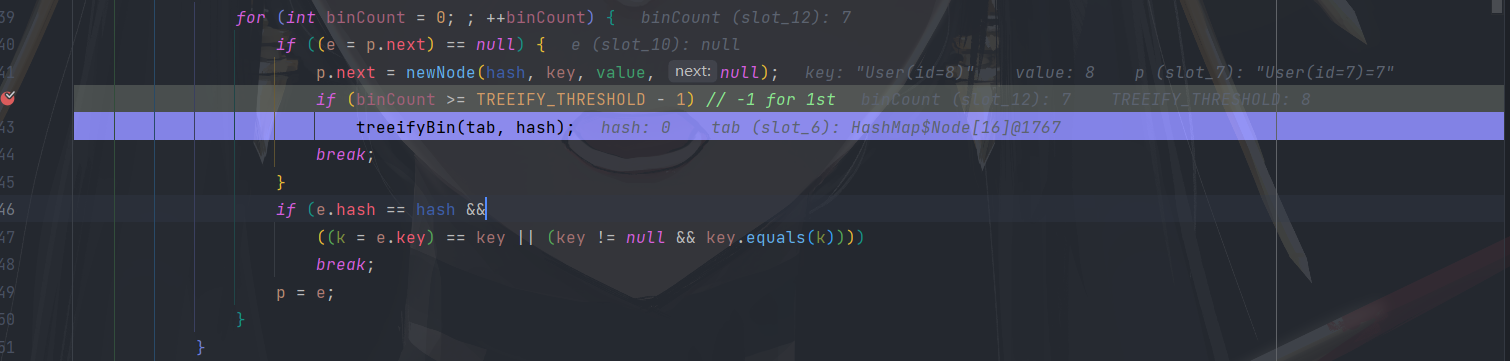
执行树化方法时发现当前 table.length < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY ( 64 ),执行一次扩容。
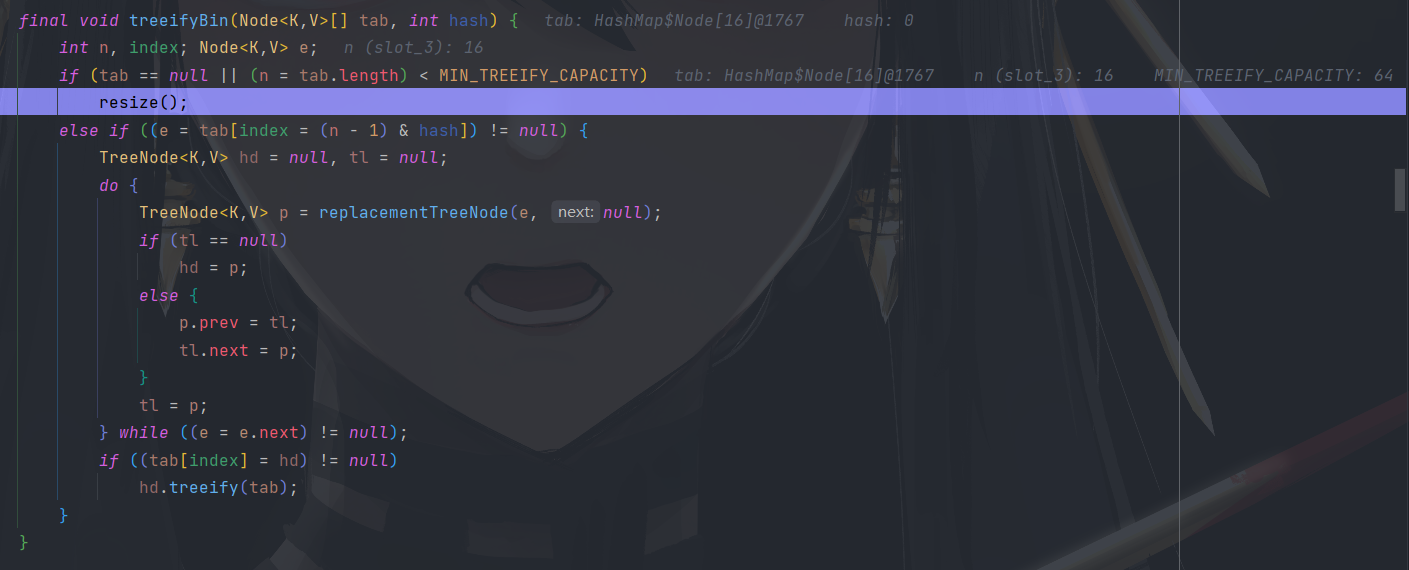
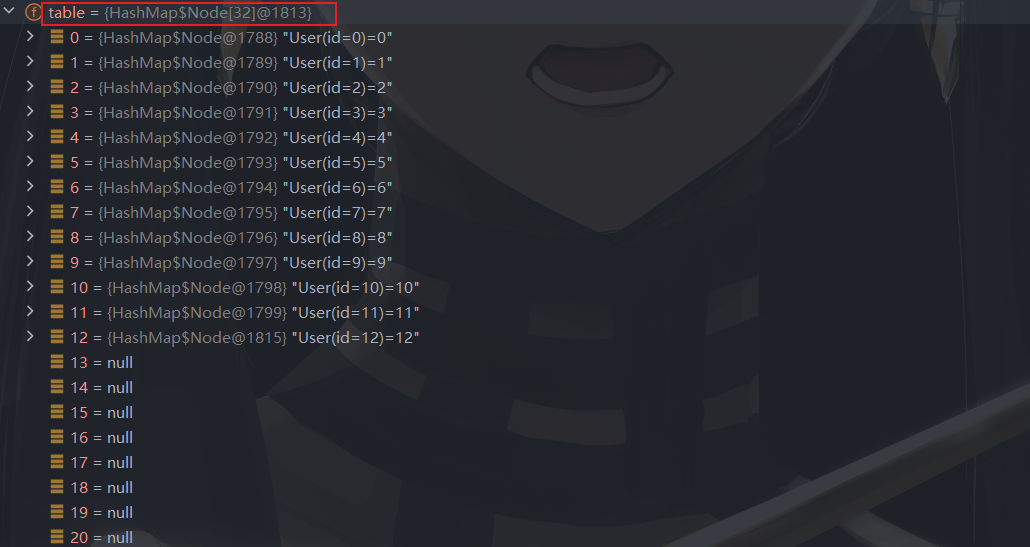
扩容后
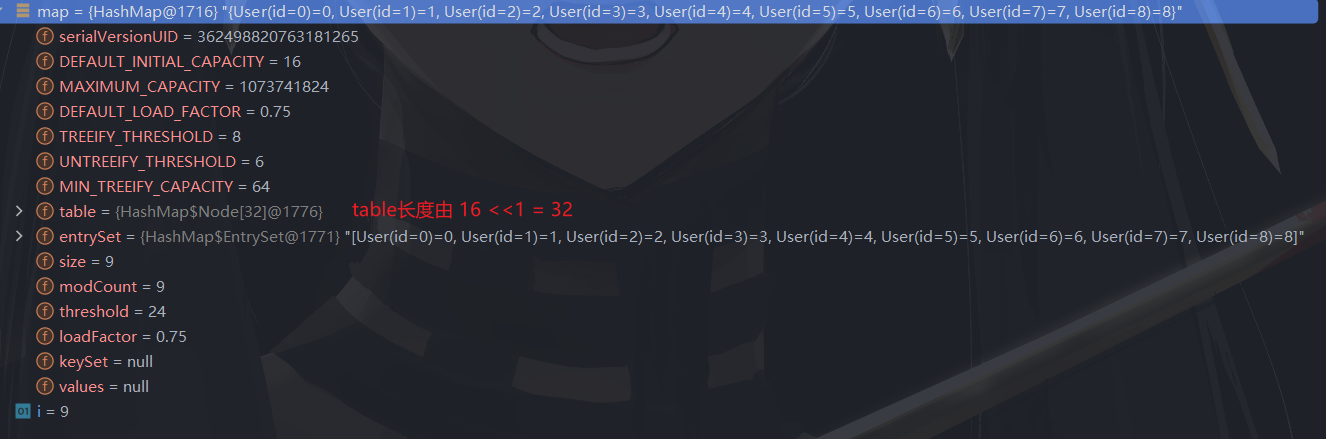
继续添加元素,与上面一样发生一次扩容

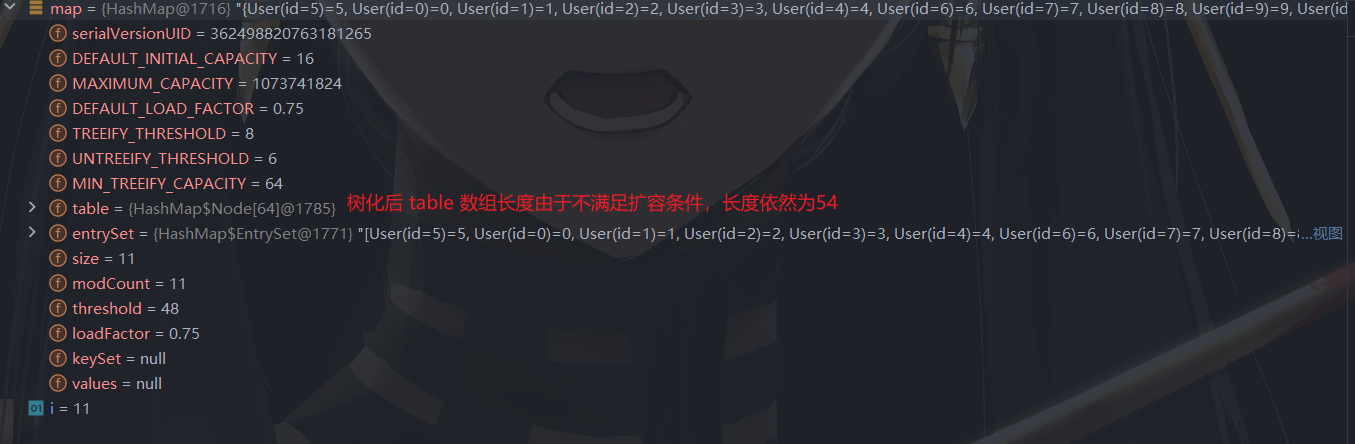
继续添加元素,此时满足树化条件,将 table [ 0 ] 进行树化(链表 -> 红黑树)。
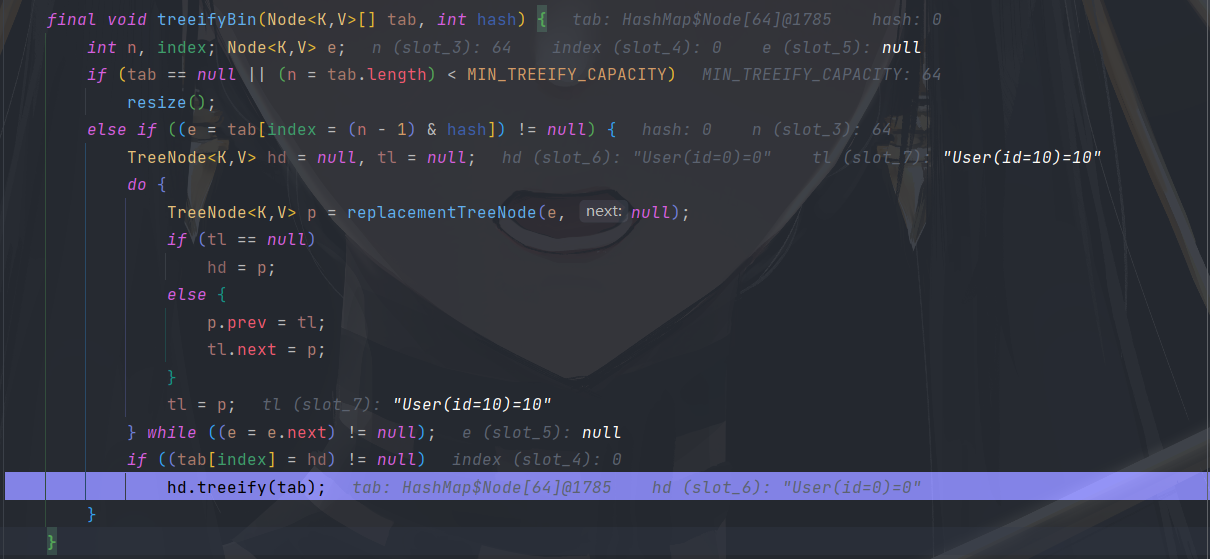
树化后:
其它
散列函数
tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]
n = table.length,将 hash 值与当前 table 长度进行取余运算,根据二进制计算特点,% 运算的效率低于 & 运算。对于 n = 2 ^ n 相当于对 ? & ( n - 1) 。
eg:
10 % 16 = 10 & 15 16 8 4 2 1 (10) 0 1 0 1 0 (15) 0 1 1 1 1 ———————————— (10) 0 1 0 1 0
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
计算散列码时将 hashcode 与其低位进行异或运算,目的是让 hashcode 高位也参与到之后的槽位计算(之前大于 table.length 的二进制位没有参与到运算),减少哈希碰撞。
java 中 hashcode 由 int 进行存储,int 为 4 个字节,32 个比特位,因此 16 为 32 的对半分。
版权声明:如无特别声明,本站收集的文章归 HuaJi66 所有。 如有侵权,请联系删除。
联系邮箱: GenshinTimeStamp@outlook.com
本文标题:《 HashMap扩容机制 》
本文链接:/java/%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95%E9%A2%98/HashMap%E6%89%A9%E5%AE%B9%E6%9C%BA%E5%88%B6.html

