已经是最新一篇文章了!
已经是最后一篇文章了!
练习-第14章_集合源码与数据结构.md
此日六军同驻马,当时七夕笑牵牛。
第14章_集合与数据结构拓展练习
选择填空题
1、前序、中序、后序遍历

分析:
完全二叉树: 叶结点只能出现在最底层的两层,且最底层叶结点均处于次底层叶结点的左侧
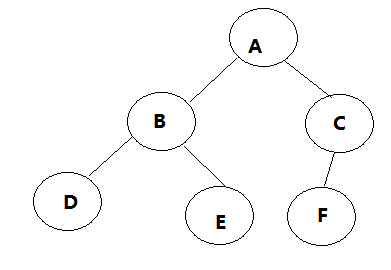
题1:
前序遍历:中左右 ABDECF
中序遍历:左中右 DBEAFC
后序遍历:左右中 DEBFCA
题2:n-i+1
2、线性结构

C
3、其它

1、先根次序遍历,就是前序遍历:
ABDHIECFG
2、队列先进先出
3、C
4、C
5、2的4次方是16个
编程题
4、单向链表构建
(1)定义一个单向链表SingleLinked类
- 包含私有的静态内部类Node
- 包含Object类型的data属性和Node类型的next属性
- 包含有参构造Node(Object data, Node next)
- 包含私有的单链表的Node类型的头结点first
- 包含public void add(Object element)方法,可以添加元素到当前单链表中
- 包含私有的非静态内部类Itr,Itr类实现java.util.Iterator接口
- 包含Node类型的实例变量node,初始化为单链表的first
- 重写boolean hasNext()方法,判断node结点是否为空
- 重写Object next()方法,获取node对象的data值,并让node结点指向下一个结点
- 单向链表SingleLinked类实现java.lang.Iterable接口,
- 重写Iterator iterator()方法,返回非静态内部类Itr的对象
(2)测试类中创建SingleLinked单链表的对象,并添加(张三、李四、王五、赵六)几个元素到单链表中,并用foreach循环变量输出。
public class SingleLinked implements Iterable{
private Node first;//单向链表的头
private static class Node{
Object data;
Node next;
Node(Object data, Node node) {
this.data = data;
this.next = node;
}
}
public void add(Object element){
Node newNode = new Node(element, null);
if(first == null){
first = newNode;
return;
}
Node node = first;
while(node.next !=null){
node = node.next;
}
node.next = newNode;
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator{
Node node = first;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return node != null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
Object element = node.data;
node = node.next;
return element;
}
}
/*
暴露静态内部类
public static class Knot{
public Object data;
public Knot next;
}
*/
}
public class Exercise4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//违反了高内聚低耦合的原则
/* SingleLinked.Knot k1 = new SingleLinked.Knot();
k1.data = "张三";
SingleLinked.Knot k2 = new SingleLinked.Knot();
k2.data = "李四";
k1.next = k2;*/
//高内聚低耦合
SingleLinked link = new SingleLinked();
link.add("张三");
link.add("李四");
link.add("王五");
link.add("赵六");
for (Object o : link) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
5、单向链表及其反转

单链表的实现
public class OneWayLinkedList<E>{
private Node<E> head;
private int total;
private static class Node<E>{
E data;
Node<E> next;
Node(E data, Node<E> next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
public void add(E e) {
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(e,null);
if(head==null){
head = newNode;
}else{
Node<E> node = head;
while(node.next!=null){
node = node.next;
}
node.next = newNode;
}
total++;
}
public void delete(E e) {
Node<E> node = head;
Node<E> find = null;
Node<E> last = null;
if(e==null){
while(node!=null){
if(node.data==null){
find = node;
break;
}
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
}else{
while(node!=null){
if(e.equals(node.data)){
find = node;
break;
}
last = node;
node = node.next;
}
}
if(find != null){
if(last==null){
head = find.next;
}else{
last.next = find.next;
}
total--;
}
}
public void update(E old, E value) {
Node<E> node = head;
Node<E> find = null;
if(old==null){
while(node!=null){
if(node.data==null){
find = node;
break;
}
node = node.next;
}
}else{
while(node!=null){
if(old.equals(node.data)){
find = node;
break;
}
node = node.next;
}
}
if(find != null){
find.data = value;
}
}
public boolean contains(E e) {
return indexOf(e) != -1;
}
public int indexOf(E e) {
int index = -1;
if(e==null){
int i=0;
for(Node<E> node = head; node!=null; node=node.next ){
if(node.data==e){
index=i;
break;
}
i++;
}
}else{
int i=0;
for(Node<E> node = head; node!=null; node=node.next ){
if(e.equals(node.data)){
index=i;
break;
}
i++;
}
}
return index;
}
public Object[] getAll() {
Object[] all = new Object[total];
Node<E> node = head;
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++,node = node.next) {
all[i] = node.data;
}
return all;
}
public int size() {
return total;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void reverse() {
if(head!=null) {
Node<E>[] all = new Node[total];
Node<E> node = head;
for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) {
all[i] = node;
node = node.next;
}
head = all[all.length-1];
node = head;
for (int i = all.length-2; i >= 0; i--) {
node.next = all[i];
node = node.next;
}
}
}
}
public class Exercise5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OneWayLinkedList<Integer> list = new OneWayLinkedList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
Object[] all = list.getAll();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(all));
list.reverse();
all = list.getAll();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(all));
}
}
6、字符串压缩

实现简易字符串压缩算法,其中连续出现2次以上(含2次)的字母转换为字母和出现的次数。
例如:AAAABCCDEEEEE,压缩之后为A4BC2DE5。
代码实现:
public class Exercise6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// String str = "AAAABCCDEEEEE";
String str = "AAAABCCDEEEEEF";
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if(list.size()==0) {
list.addLast(str.charAt(i)+"");
count++;
}else {
if(list.getLast().equals(str.charAt(i)+"")) {
count++;
}else {
if(count>1) {
list.addLast(count+"");
}
list.addLast(str.charAt(i)+"");
count=1;
}
}
}
if(count>1) {
list.addLast(count+"");
}
while(list.size()!=0) {
System.out.print(list.pollFirst());
}
}
}
版权声明:如无特别声明,本站收集的文章归 HuaJi66/Others 所有。 如有侵权,请联系删除。
联系邮箱: GenshinTimeStamp@outlook.com
本文标题:《 练习-第14章_集合源码与数据结构.md 》

